How It Works
A self-contained solution
Take a tour of the teaching system delivering practical surveillance training to any PC without the need for instructor oversight or specialised hardware.
Expert Teaching
Carefully curated video lessons and training exercises targeting essential skills in surveillance control.
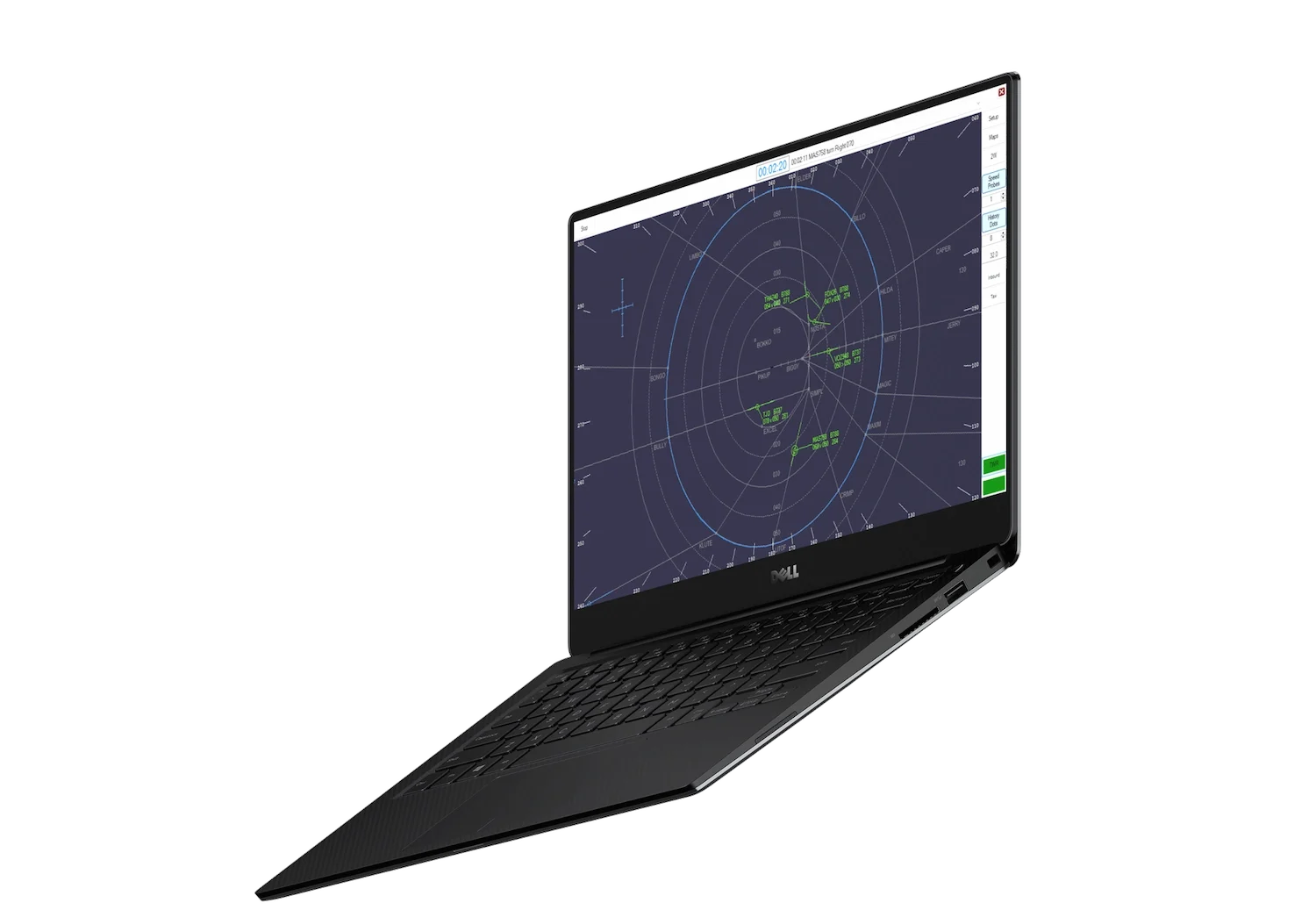
Standalone Simulation
The personal teaching simulator. Featuring independent operation and automatic performance tracking – no pseudopilots required.
Flexible Delivery
Access training anywhere with Control Zone, the cloud hub for Visual Vectoring courseware and time-saving administration tools.
How we help
Your training capability multiplier
Access equals opportunity. Discover how on-demand simulation can elevate training, lower costs and expand curriculum at your organisation.
ANSPs and ATC Training Providers
Improve Outcomes
Provide a low-pressure environment for trainees to develop confidence and consolidate core skills during early training.
Optimise Infrastructure
Enhance the availability and efficiency of existing simulator equipment.
Empower Instructors
Equip the experts with data-driven insights into student performance and additional opportunities for one-on-one mentorship.
Higher Education & Universities
Lead the Field
Provide every student with access to industry standard simulation training at low cost and without the need for specialised equipment.
Flexible Delivery
Teach your way with a cloud delivery platform that supports remote learning and a range of on-campus applications.
Readymade Courseware
Simplify curriculum design with a suite of readymade surveillance courses designed by experienced instructors.
TESTIMONIALS
What our Partners say




Become a Partner
Join a global community of institutions transforming their teaching capacity with on-demand simulation training.
Get started todayCourses
A comprehensive curriculum at your fingertips
Training thousands of prospective Approach Controllers how to manage a busy sequence to the runway.
Covering fundamental skills in surveillance control – ideal for students experiencing ATC for the first time.
Teaching the complex skill set required to manage an arrivals sequence with the use of holding, vectoring and time requirements.
A training capstone: teaching the simultaneous management of mixed departures and arriving traffic.
The most effective way to deliver targeted competency training for the response to a compromised separation event.
Helping thousands of students around the world
Latest news & insights
Stay up to date with the latest developments from Visual Vectoring and our training partners